New technique to detect tropical cyclones earlier than satellites
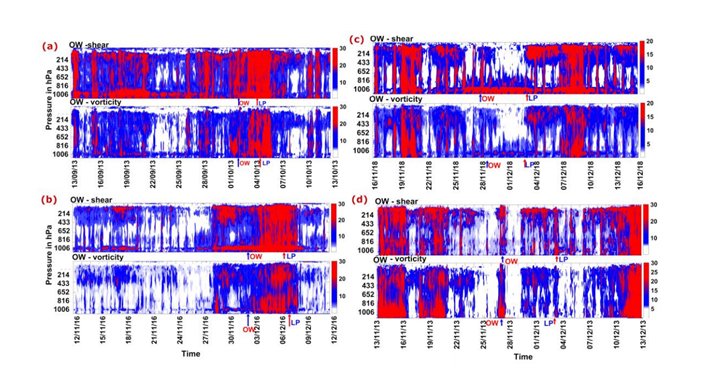
New Delhi: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur have developed a technique that could be useful in the early detection of development or strengthening of tropical cyclones in the atmospheric column prior to satellites over ocean surface in the North Indian Ocean region. Researchers devise a novel method using Eddy detection technique to investigate the formative stages and advance detection time of tropical cyclogenesis in the North Indian Ocean region. This study has been conducted under the Climate Change Program (CCP) with the support from Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, an official statement said. Early detection of…