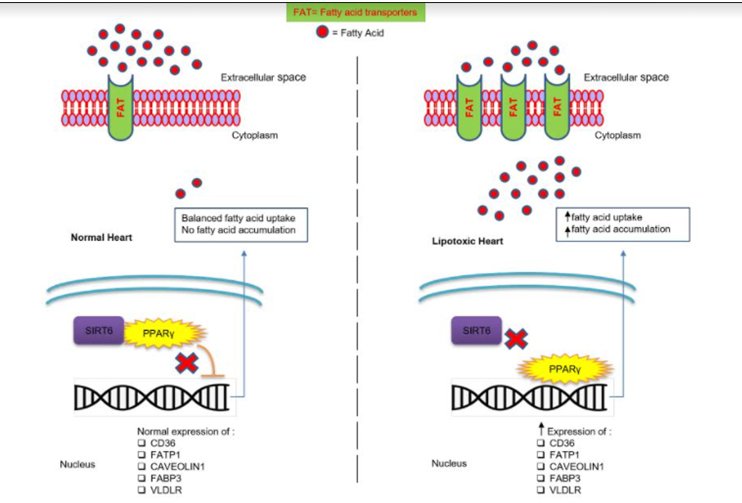
Study could help unravel mystery of fatty acid accumulation in heart
New Delhi: Fatty acids are formed when the fat in our diet breaks down during digestion. While many of the body’s organs use glucose as their primary energy source, the heart derives most of its required energy (over 70%) from the oxidation of fatty acids. These are crucial for sustaining cardiomyocytes – cardiac muscle cells that control the rhythmic beating of the heart. However, the accumulation of excess fatty acids in cardiomyocytes triggers harmful responses, often leading to severe cardiac diseases. A recent study published in Cell Reports by a team of researchers from India and the US, led by scientists at the Indian…